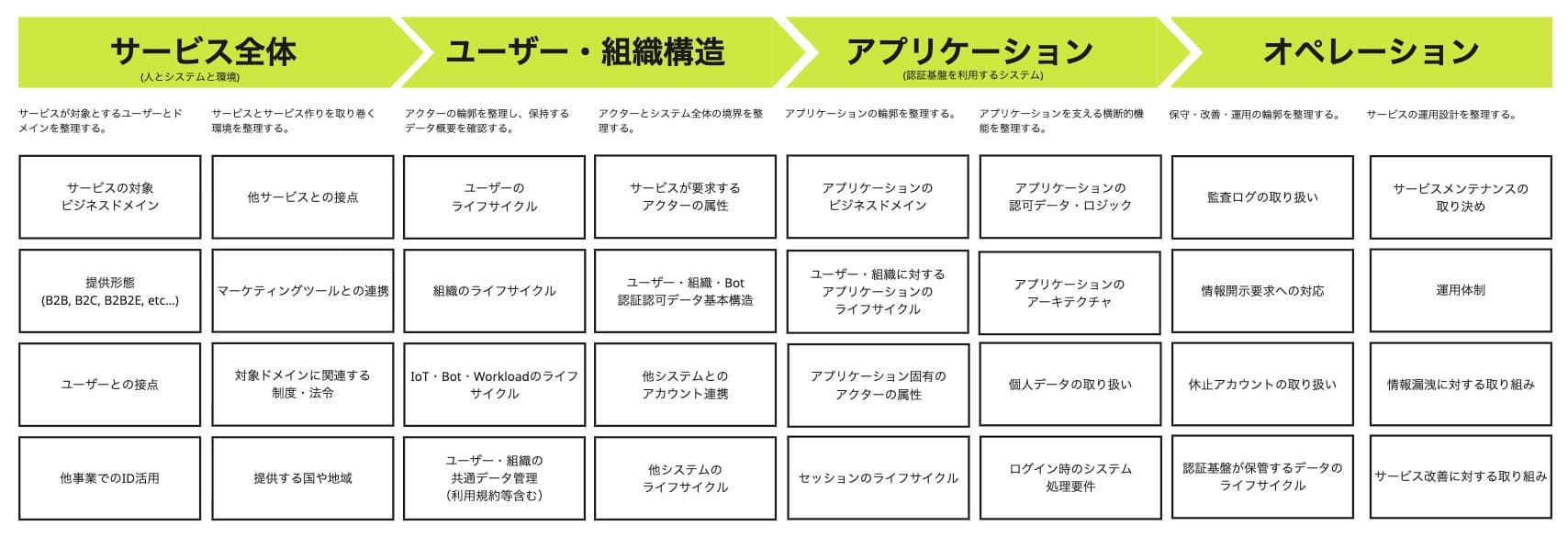
Customer ID Consolidation: Its Importance in Modern Digital Business and Path to Success
目次
The Importance and Path to Success in Modern Digital Business
With the rapid advancement of digital technology, the number of IT and web services offered by businesses continues to grow exponentially, along with the vast amounts of customer data that must be managed. Against this backdrop, customer ID consolidation has emerged as an essential strategic approach for companies to maintain competitiveness and achieve sustainable growth. This system, which enables centralized management of customer IDs that were previously scattered across multiple systems and platforms, offers benefits far beyond mere operational efficiency—providing significant advantages for both customers and businesses alike.
The Contemporary Significance of Customer ID Consolidation
In today's marketing landscape, omnichannel engagement—where businesses interact with customers across multiple channels including e-commerce sites, physical stores, smartphone apps, and websites—has become the norm. Furthermore, strategies like OMO (Online Merges with Offline) and O2O (Online to Offline) that integrate online and offline channels are gaining widespread adoption. To ensure seamless customer experience (CX) across these diverse channels, customer ID consolidation has become absolutely essential.
Here's why customer ID integration holds particular importance in modern business practices:
1. Enhanced Customer Experience and Increased Convenience

Customers no longer need to register and manage separate IDs and passwords for each service or platform provided by a single company. The implementation of single sign-on (SSO) functionality allows users to access multiple services with a single authentication, eliminating login hassles and significantly improving usability. This prevents users from abandoning services during transitions between them and contributes to higher customer retention rates.
"Disjointed experiences" where behavior and purchase history across multiple channels don't connect properly can leave customers feeling frustrated and dissatisfied, ultimately diminishing brand trust and purchase intent. ID integration resolves such communication gaps.
2. Optimized Personalized Services and Marketing Strategies

Through ID integration, companies can centrally manage customers' behavioral history and preferences, enabling them to deliver highly personalized services and targeted promotions tailored to individual users. This enhances customer engagement and contributes to increasing customer lifetime value (LTV).
By establishing a Single Customer View (SCV), different departments can base their initiatives on unified customer data, leading to optimized marketing strategies and more efficient service delivery.
3. Improved Data Management Efficiency and Enhanced Security Measures

Centralizing customer data that was previously scattered across different systems and platforms helps maintain data integrity while reducing management costs. This prevents data silos and ensures data accuracy and consistency.
Strengthening security is another significant benefit. Integrated identity management reduces the risk of unauthorized access, making it particularly important in today's era of stringent data protection requirements. The implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA) and passwordless authentication methods like passkeys not only improves security but also enhances the customer experience.
4. Compliance with Privacy Regulations
When implementing identity integration, compliance with privacy laws and regulations is imperative. Adherence to data protection laws including GDPR and other national regulations is critically important for maintaining corporate credibility. Proper security measures such as data anonymization and encryption must be implemented, along with clearly defined processes for obtaining customer consent and ensuring transparency. Providing functionality that enables customers to request disclosure, correction, or deletion of their data is also essential.
Methods and Approaches for Identity Integration
There are two primary approaches to identity integration: company-led implementation and customer-led implementation.
1. Company-Led Identity Integration
The most common method is to consolidate existing customer IDs into a single unified ID.
- Deterministic matching (deterministic integration)
This method combines data entries that match exactly in terms of information such as name, email address, or phone number, treating them as belonging to the same customer. This approach is effective when data accuracy is high and is suitable for "error-intolerant" scenarios like email delivery and billing processes.
- Probabilistic matching (stochastic integration)
Using AI technology and machine learning, this method identifies and combines data entries that are highly likely to be from the same customer, even when the data only partially matches. This approach enhances integration accuracy even when data is incomplete, making it ideal for scenarios where "maximizing reach" takes priority over absolute accuracy, such as advertising delivery or analyzing anonymous users before registration.
2. Customer-Led Identity Integration
This approach involves maintaining each service's existing customer IDs while encouraging customers to create and link new IDs to their existing ones. By utilizing systems equipped with SSO (Single Sign-On), MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication), and SNS integration features, you can improve customer convenience while reducing the burden of managing multiple passwords.
4 Key Steps for Successful Customer ID Integration

While many companies struggle with customer ID integration, the following four practical steps can help ensure success. Particularly, connecting online and offline data remains a complex challenge for most businesses.
Step 1: Current status assessment of existing data
First, thoroughly identify all customer IDs scattered across your organization—including website membership IDs, app login IDs, and store membership numbers—and organize where each type of information is located. Insufficient assessment of this current status can lead to integration omissions or reduced accuracy.
Step 2: Designing Customer ID Mapping
Develop a strategy for "which information will be used to connect customer IDs." This requires designing both deterministic methods (using clear, definitive information for integration) and probabilistic methods (making estimates based on browsing history and behavioral patterns), choosing the appropriate approach depending on your objectives and intended use cases.
Step 3: Data Cleansing and Deduplication
Before integrating customer IDs, clean and organize your data to address issues like inconsistent formatting, duplicate entries, and missing information. Since inaccurate data itself cannot achieve high integration accuracy, implementing both automated processing tools where possible and manual verification when needed is crucial for effective data cleansing and deduplication.
Step 4: Establishing Integration and Utilization Frameworks
Using the prepared data and integration rules, actually connect customer IDs and prepare the data for marketing use. Cross-platform integration across multiple data sources and the establishment of operational frameworks for utilizing integrated IDs are key to successful implementation.
Key Considerations and Challenges in ID Integration Implementation
There are several important considerations and challenges when implementing ID integration:
- Data infrastructure development
Building a robust data infrastructure is essential to prevent data silos and enable centralized management through a single customer view (SCV).
- Compliance with privacy regulations
Adherence to privacy laws including GDPR is crucial for maintaining corporate credibility, requiring clear processes for data anonymization, encryption, and obtaining customer consent.
- Handling irregular cases
It's common to overlook potential irregular use cases that can't be fully anticipated. Conducting detailed interviews and workshops from multiple perspectives, along with forward-looking scenario planning for potential future business environments, can be highly effective.
- Security vs. usability trade-offs
Security levels and usability are fundamentally in opposition, requiring careful balancing. Consulting with IT departments and external experts is recommended, with thorough risk analysis and countermeasures being essential.
- Collaboration with organizational and service operations
ID integration goes beyond mere system efficiency to impact business operations and processes. Rather than issuing unilateral directives from project teams, successful implementation requires respecting and closely collaborating with frontline operations to understand their specific circumstances and needs.
Solutions Supporting ID Integration
For organizations dealing with massive amounts of data, utilizing specialized solutions designed for ID integration is strongly recommended.
- Customer Identity and Access Management (CIAM) solutions
CIAM tools provide cloud-based solutions for managing customer IDs and data, implementing SSO, MFA, passwordless authentication, user-controlled data management, and data integration. These CIAM solutions help achieve business objectives such as acquiring new customers, improving LTV, complying with privacy regulations, and enhancing security. Leading examples include "SAP CIAM" and "Auth0."
SAP CIAM has been implemented by companies including Kao Corporation's My KAO and SEIBU Holdings' SEIBU Smile ID (link), while Auth0 has been adopted by SUBARU, Chubu Electric Power, NTT DoCoMo, and the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry.
These solutions enable integration of brand-specific e-commerce sites, simplifying control over diverse information and features through customer ID linking. They also reduce operational burdens in ID management, establish foundations for fan marketing, and facilitate service integration across group companies.
Across various clients, TC3 has achieved numerous successful implementations, including common ID management platforms for MS&AD InterRisk Research & Consulting and G-Search, a Fujitsu Group company.
- CDP (Customer Data Platform)
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) is a platform designed to collect, manage, and analyze individual customer data, making it ideal for leveraging customer data in marketing applications. In addition to standard customer data such as name, age, and purchase history, it enables integration of various data types—including web/app behavior data and offline store data—all linked back to individual customer IDs.
Hightouch: Often referred to as a "composable CDP," Hightouch is a data utilization platform that maximizes the value of data stored in data warehouses. Hightouch's ID integration functionality allows easy verification of how customer ID integration is being implemented while offering flexible customization options. It also supports different logic configurations for specific use cases—such as "for accurate email delivery" versus "for broad advertising reach," and all data is securely stored in your proprietary data warehouse. The platform's API integration capabilities are highly valued for their versatility and scalability.
Summary
Customer ID integration has become essential in today's digital era, enabling businesses to deepen their understanding of customers, unify their customer experience (CX), and achieve a single customer view. This enables the delivery of personalized services, optimization of marketing strategies, and improvement in customer lifetime value. At the same time, it also helps address key business challenges including more efficient data management, enhanced security, and compliance with privacy regulations.
Successful implementation relies on the proper combination of deterministic and probabilistic matching methods, along with careful execution of steps such as customer ID inventory management, data cleansing, and deduplication. Utilizing specialized systems and platforms like CIAM solutions and CDPs (particularly composable CDPs like Hightouch), and leveraging the expertise of external specialists when necessary, can help smoothly navigate complex customer ID integration projects.
By implementing an optimal ID integration system and establishing a robust data foundation to support business growth, you can build lasting customer relationships and drive corporate performance improvements.
.png&w=3840&q=75)